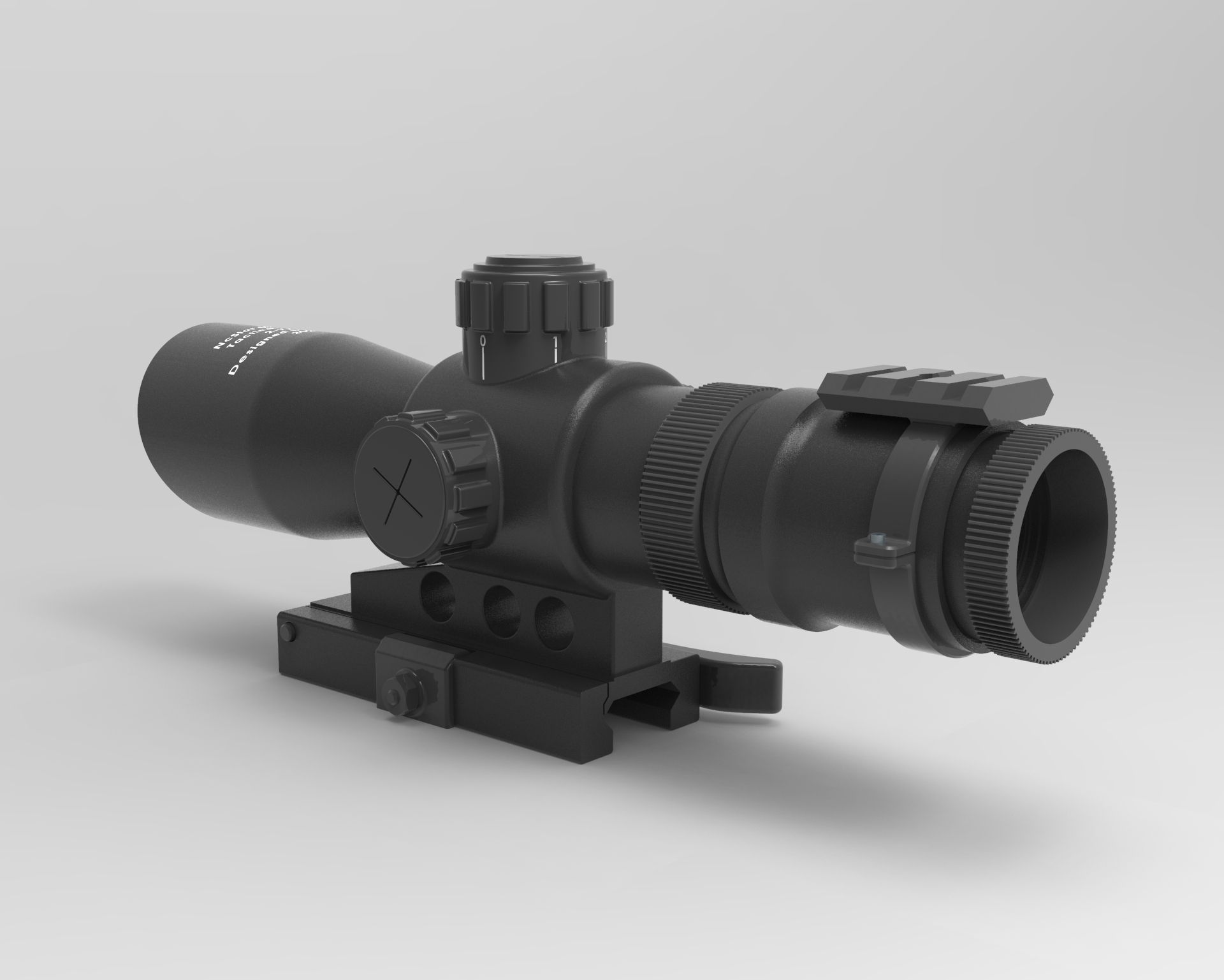
The Significance of Small Dimensions in the Manufacturing Sector

The Basics of Small Dimensions in CNC Manufacturing
The Importance of Precision

Challenges
- Material Behavior: Different materials react differently under machining processes, especially at micro-level dimensions. For instance, metals might expand or warp under heat, while plastics may exhibit different characteristics based on their composition. This variability can make achieving consistent precision a challenging task.
- Tooling Accuracy: The precision of CNC machines heavily relies on the accuracy of the tools used. At small dimensions, even the slightest wear and tear on a tool can lead to significant deviations in the final product. Regular monitoring and maintenance of tools are crucial to ensure ongoing precision.
- Environmental Factors: Factors like temperature, humidity, and even minute vibrations in the manufacturing environment can impact the accuracy of CNC machining at small scales. Precision engineering requires controlled environments where such factors are meticulously managed.
- Human Error: Despite the high level of automation in CNC machining, human oversight is still essential. The programming of machines, setting up of tools, and quality control processes are susceptible to human error, which can affect the precision of the final product.
Benefits
- Superior Performance: Products manufactured with high precision, especially in small dimensions, often exhibit enhanced performance. For instance, in the aerospace industry, the precise machining of engine components can lead to more efficient fuel consumption and improved overall performance of the aircraft.
- Longer Product Life: Precision engineering contributes to longer life spans of products. Components that are accurately machined fit better, wear down less, and therefore last longer. This is particularly crucial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where component longevity is directly linked to safety and efficiency.
- Higher Reliability: When products are manufactured with precision, they are more reliable. In the medical field, for example, the accuracy in manufacturing medical devices such as implants or surgical instruments directly impacts their reliability, which in turn affects patient outcomes.
- Meeting Stringent Standards: Many industries have strict regulatory standards for product dimensions and tolerances. Precision engineering at small scales ensures that these standards are met, which is essential for companies to stay compliant and competitive in the market.
- Innovation and Design Freedom: With the ability to achieve high precision, designers and engineers are free to innovate and create more complex and sophisticated products. This has led to the development of new products and technologies that were previously thought impossible due to manufacturing limitations.
The Role of Tolerances in Manufacturing
Technological Advancements and Small-Dimension Manufacturing
The evolution of CNC technology has been pivotal in achieving the high precision required for small dimensions. Modern CNC machines are equipped with advanced features like high-speed spindles, multi-axis movement, and sophisticated software control, enabling them to handle complex geometries with incredible accuracy. These advancements not only improve the precision but also significantly reduce the time and cost involved in the manufacturing process.
Ethereal Machines, India’s leading in the CNC machining industry, stands at the forefront of this precision revolution. We specialize in providing cutting-edge CNC solutions tailored to the needs of various industries. With a fleet of state-of-the-art CNC machines and a team of skilled engineers, we are equipped to handle the most challenging precision requirements.
The Impact of Small Dimensions on Design and Engineering
Design and engineering practices must adeptly navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by small dimensions. Meticulous planning and simulation are prerequisites to ensure that the manufacturing process can achieve the necessary precision without incurring excessive costs or time delays. This section intricately discusses the delicate relationship between small dimensions, design, and engineering and the imperative role each plays in the pursuit of precision.
Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities
- Intricate Planning and Simulation: In the realm of small dimensions, every aspect of design and engineering requires meticulous planning. Advanced simulation tools are employed to predict how designs will behave under real-world manufacturing conditions. This includes assessing the material properties, understanding tooling limitations, and anticipating environmental impacts on the final product. Simulations help in identifying potential issues early in the design phase, reducing the risk of costly revisions later.
- Precision-Driven Design Choices: Engineers and designers must make conscious decisions that account for the capabilities and limitations of precision machining. This often involves selecting materials that are more stable and predictable under small-scale machining and designing parts that can be accurately and reliably produced. Features such as tiny grooves, ultra-fine threads, or complex 3D shapes, which were once considered unfeasible, are now achievable thanks to advancements in precision engineering.
- Collaboration Between Design and Manufacturing: There’s a heightened need for close collaboration between designers and manufacturing teams. Designers need to have a thorough understanding of CNC machining capabilities and constraints, while manufacturers must stay abreast of the latest design trends and technologies. This synergy ensures that designs are not only innovative but also manufacturable.
- Cost and Time Considerations: Achieving precision in small dimensions often comes with increased costs and longer production times. Designers and engineers must balance the need for precision with economic viability. This involves optimizing designs for manufacturability to minimize waste, reduce machining time, and ultimately lower production costs.
- Adapting to Rapid Technological Advancements: The field of precision engineering is evolving rapidly. Design and engineering practices must continuously adapt to new technologies and processes. This requires ongoing education and training, as well as investment in state-of-the-art equipment and software.
The Imperative Role of Precision in Design and Engineering
- Quality and Performance: Precision in small dimensions is critical for the quality and performance of the final product. In industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where the margin for error is minimal, the precision of small components can have a significant impact on the overall functionality and safety of the system.
- Enabling Innovation: Precision engineering has expanded the horizons of what is possible in design and product development. Designers now have the freedom to explore complex geometries and intricate details that were previously impossible, opening up new avenues for innovation and creativity.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that excel in precision engineering often gain a competitive edge in the market. Being able to produce highly precise and reliable components can be a key differentiator, especially in sectors where quality and accuracy are paramount.
- Sustainability Considerations: As the focus on sustainability grows, precision engineering plays a crucial role. By enabling the efficient use of materials and energy, and by extending the lifespan of products through higher quality, small dimensions in design and engineering contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Quality Control in Small Dimensions
Ensuring quality in small dimensions poses unique challenges that demand sophisticated inspection methods. Laser scanning, coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), and computerized tomography (CT) scans are employed to guarantee that products meet stringent specifications. This section delves into the complexities of quality control in small-dimension manufacturing and highlights the sophisticated measures employed to uphold the highest standards.
Material Considerations in Small-Dimension Manufacturing
The material chosen for small-dimension parts significantly influences their manufacturability and performance. Manufacturers must meticulously consider factors such as thermal expansion, material consistency, and machining characteristics to achieve precision in small-dimension manufacturing. This section explores the intricate balance between material science and precision engineering, emphasizing the importance of material selection in achieving optimal results.
The Imperative Role of Precision in Design and Engineering
As products become increasingly miniaturized and complex, the challenges associated with small dimensions are magnified. Future trends may include the integration of nanotechnology and the development of new materials and techniques to achieve even greater precision. This section provides an insightful exploration of the evolving landscape of small-dimension manufacturing, addressing both the challenges and opportunities it presents. The integration of emerging technologies and innovative approaches is discussed as a pathway to overcoming the hurdles associated with precision engineering.
The Professional Approach to Small-Dimension Manufacturing
A professional approach to small-dimension manufacturing requires a meticulous blend of expertise, innovation, and commitment to quality. This section emphasizes the importance of cultivating a culture of continuous improvement, where professionals embrace challenges as opportunities for growth. It underscores the need for interdisciplinary collaboration, where experts in technology, material science, design, engineering, and quality control collaborate seamlessly to achieve the highest standards of precision.
Conclusion
In summary, the meticulous attention to small dimensions in manufacturing epitomizes a steadfast commitment to precision and excellence. Despite their seemingly subtle nature, small dimensions pose a significant challenge and opportunity. The professional approach to small-dimension manufacturing ensures that precision remains central, driving innovations for sophisticated, reliable, and accessible products. The industry’s dedication to continuous improvement guarantees that small dimensions will persist as a pivotal focal point, inspiring advancements that redefine precision engineering. Looking forward, the legacy of small dimensions in manufacturing will continue to shape a future where excellence is synonymous with the relentless pursuit of precision.
On-demand CNC Machining Services by Ethereal Machines offers the perfect solution for your CNC machining needs. With secure and confidential processes, you can get an instant quote and access expert advice from their technical team. Whether you need custom CNC machined parts or have a specific project in mind, Ethereal Machines is committed to helping you every step of the way. Try MAAS now and achieve your goals with ease.
Views: 595
















